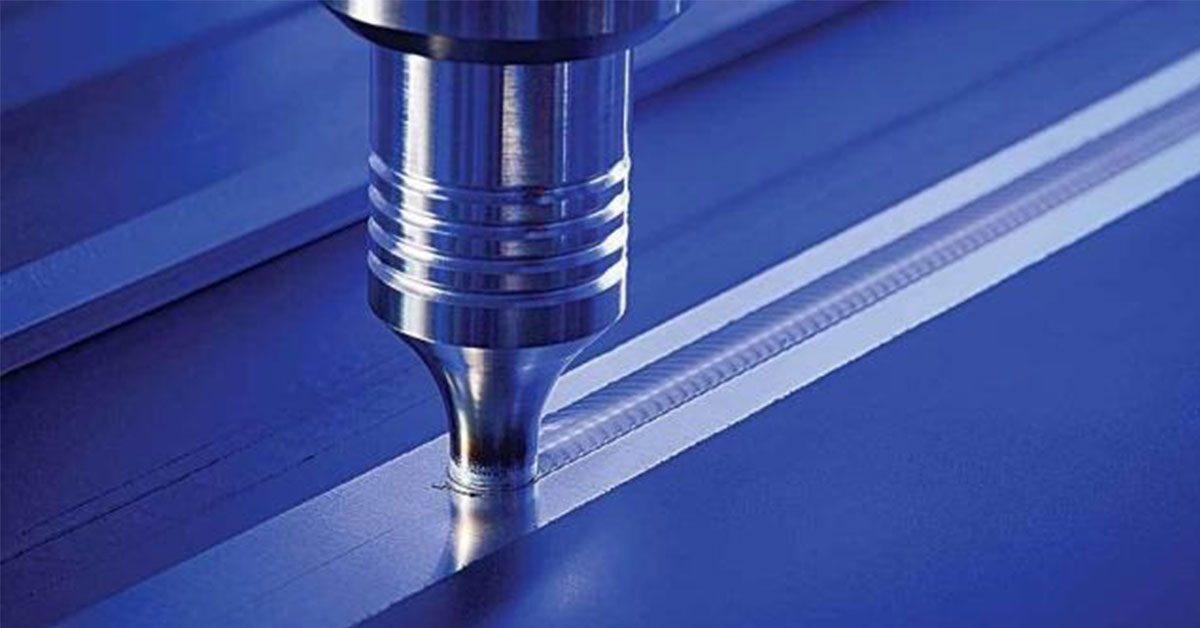
Welding Methods for 304 Stainless Steel Pipes
Characteristics of 304 stainless steel pipe
304 stainless steel pipes are renowned for their excellent mechanical properties, including high strength and good ductility. They exhibit a yield strength exceeding 205 MPa and a tensile strength surpassing 520 MPa, with an elongation of over 40%. Compared to the 200 series stainless steels, 304 stainless steel offers superior rust resistance and performs well at high temperatures, withstanding up to 1000-1200°C.
Cooling Methods for 304 Stainless Steel Pipes
Cooling methods for 304 stainless steel pipes are relatively straightforward, typically involving air cooling or water cooling, with water cooling being the most common. The maximum temperature achievable during cooling is between 1080°C and 1100°C. During cold processing, temperatures can be reduced to between 850°C and 970°C, followed by insulation and then water cooling to complete the process.

Applications of 304 Stainless Steel Pipes
1. Chemical Industry: In the chemical industry, 304 stainless steel pipes are extensively used for transporting various media, including dilute acids, concentrated acids, hydrochloric acid, hydrofluoric acid, sodium hydroxide, and potassium hydroxide.
2. Petroleum Industry: In petrochemical applications, 304 stainless steel pipes are commonly employed for transporting high-temperature and high-pressure substances such as oil and natural gas.
3. Pharmaceutical Industry: The pharmaceutical sector uses 304 stainless steel pipes widely for transporting various pharmaceutical liquids, liquid impregnation processes, and filtration operations.
4. Aerospace Industry: In aerospace, 304 stainless steel pipes have numerous applications, including in aircraft engine exhaust systems, engine intake systems, and hydraulic pipelines.
304 stainless steel pipes are a common material widely used in construction, chemical, petroleum, pharmaceutical, and food industries. Welding is an essential process when working with stainless steel pipes for engineering projects. This article will discuss the welding methods and considerations for 304 stainless steel pipes.

I. Welding Methods
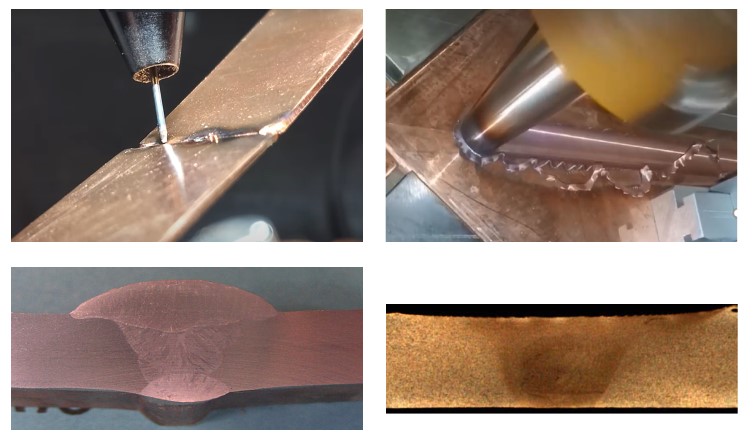
The primary welding methods for 304 stainless steel pipes include manual arc welding, tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding, and plasma arc welding. Below is a detailed overview of these three methods.
1. Manual Arc Welding
Manual arc welding is a commonly used method suitable for various sizes of 304 stainless steel pipes. The process involves aligning the two ends of the stainless steel pipe and welding with an electrode. It's crucial to maintain arc stability and select an electrode that matches the material of the stainless steel pipe. Additionally, controlling welding speed and temperature is essential to prevent welding defects.
2. TIG Welding
TIG welding is a gas shielded welding method favored for its high-quality results, especially for 304 stainless steel pipes that demand superior welds. During TIG welding, a protective sleeve is first added to the welding area of the stainless steel pipe, followed by the use of argon gas to shield the weld from oxygen and moisture. It's important to maintain arc stability, choose appropriate welding current, and ensure a moderate welding speed to achieve optimal results.
3. Plasma Arc Welding
Plasma arc welding is a high-energy welding technique suitable for thicker 304 stainless steel pipes. The process involves preheating the welding area of the stainless steel pipe and then using a plasma arc for welding. Plasma arc welding is characterized by its high energy and speed, allowing for deeper penetration and higher quality welds. However, plasma welding equipment is relatively expensive and complex, requiring skilled operators.

II. Welding Considerations
When welding 304 stainless steel pipes, several key considerations must be observed:
1. Surface Cleaning: Before welding, ensure that the welding area of the stainless steel pipe is thoroughly cleaned to remove contaminants such as oil, dust, and debris. This step is crucial to avoid compromising the welding quality.
2. Heat Input Control: It's important to control the heat input during welding to avoid excessively high temperatures and welding speeds that can lead to defects such as porosity or slag inclusion.
3. Choosing the Right Welding Material: Select welding materials that match the stainless steel pipe's composition to ensure good welding quality. Also, proper storage and protection of welding materials are necessary to prevent moisture absorption and oxidation.
4. Controlling Welding Distortion: Welding can cause thermal distortion, so it's important to manage welding deformation. Techniques such as alternating welding and local preheating can help mitigate distortion.
5. Post-Weld Treatment: After welding, post-weld treatments are necessary to relieve residual stresses and enhance the corrosion resistance of the weld. Common post-weld treatments include annealing and solution treatment.
In summary, welding methods for 304 stainless steel pipes include manual arc welding, TIG welding, and plasma arc welding. Key considerations include surface cleaning, controlling heat input, selecting appropriate welding materials, managing welding distortion, and performing post-weld treatments. By following the correct welding methods and considerations, you can ensure high-quality welds for 304 stainless steel pipes, enhancing the safety and reliability of engineering projects.
Do you want to know about FSW welding?