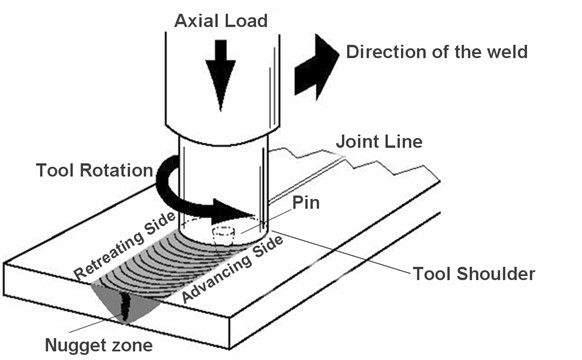
friction stir welding, FSW
Northwestern Polytechnical University discovered abnormal fracture form of thick plate friction stir welding joint
Compared with the common thick-plate defect-free aluminum alloy friction stir welding (FSW).
The fracture form of the 7 series high-strength aluminum alloy FSW joint is that the crack starts from the middle of the surface layer of the weld nugget (WNZ), and spreads to fracture, rather than The heat-affected zone (HAZ) where the joint is the weakest is broken.
Recently, Professor Weifeng Xu (corresponding author) of Northwestern Poly technical University etc. welded 12mm thick 7085-T7452 aluminum alloy plate by FSW method.
The experiment found that the high-strength aluminum alloy FSW joint was abnormally fractured. The relevant results were published in the Journal of Materials Research and Technology under the title of "Abnormal fracture of 7085 high strength aluminum alloy thick plate joint via friction stir welding". Thesis connection: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.09.077

The author studied the change of the crack propagation path of the overall defect-free joint and the delaminated (top, middle, and bottom) joints which are welded by FSW at room temperature tensile test.
And the test shows that the strength and elongation at break of the whole and slice joints are reduced compared to the base material (BM).
In particular, the whole joint and the top slice crack after the yield point or even without yielding.
The whole joint and top slice fractures in a zigzag manner at WNZ, and the middle and bottom joints fracture at 45° at the weakest area (HAZ).

Fig. 1 - Macroscopic fracture of whole (a) and slices (b) of 7085aluminum alloy FSW joints.

Fig. 2 - EBSD misorientation color maps of the BM (a), top (b), middle (c) and bottom (d) of WNZ, HAZ (e) of joint.

Fig. 3 - Experimental DIC contour maps of principal strain at different stages (a) whole joint, (b) top slice,
(c) middle slice and (d) bottom slice.
In general, the microhardness distribution and microstructure characteristics are not the main causes of the abnormal fracture in WNZ for the whole joint and the top slice.
The main reason is that the strain is concentrated in the WNZ of top slice.
While there is no strain concentration can be found in WNZs of both middle and bottom, and as the stress increases, the strain in HAZ increases uniformly.
During the stretching process, the whole joint and the top slice joint cracked in WNZ, the middle and bottom slices joints cracked in the HAZ, which eventually led to the fracture of the corresponding area.