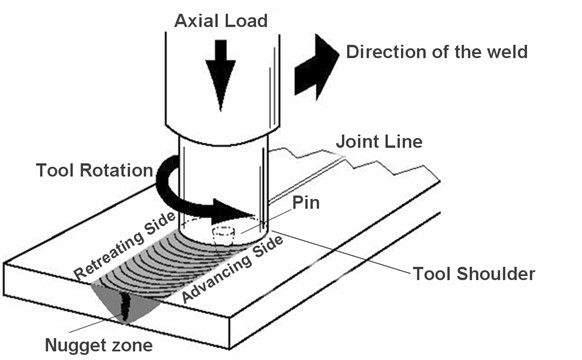
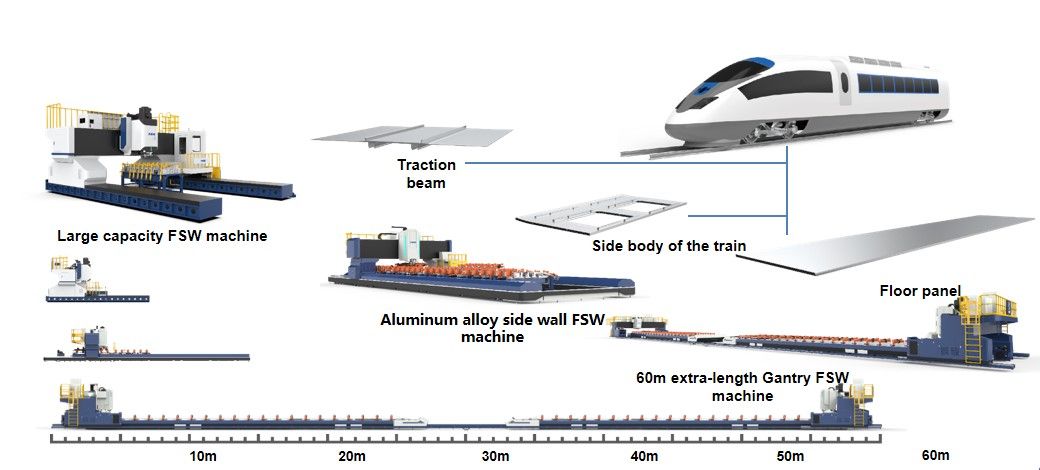
Automotive lightweight

Figure 1 Functional relationship between weight and cost
In FIG. 1, the vertical axis is cost and the horizontal axis is weight. From the horizontal axis, it can be divided into three areas. In the first area, as the weight is reduced, the cost is also reduced. In this area, the weight is still at a higher stage; in the second area, the weight is further reduced, the cost will also be reduced, until the lowest cost The pole of this is an optimal point for light weight. After this pole, the weight is further reduced, and the cost is increased. The horizontal axis also enters the third area from the second area; in the third area, the light weight is further increased. In-depth, the cost has also increased dramatically.
If cost and weight are regarded as the objective function of the entire vehicle, and function, performance, durability, etc. are regarded as the boundary conditions of this objective function system, then the way of lightweighting is its function influencing factors, and it is necessary to use the optimization method to calculate The pole of the objective function. In order to understand the extreme value, we can start from two aspects at the same time: one is to optimize the geometric size (topology optimization), the design safety factor, and the material to optimize; the second is to use lightweight materials, such as high-strength steel, aluminum alloy, and magnesium New materials such as alloys and carbon fibers.
Min. cost = fc (geometry, shape, material, manufacturing process)
Min. weight = fw (geometric size, shape, material, manufacturing process)
Compared with other lightweight materials, high-strength steel has a low price and good economy. Wide application can improve the safety of the car. High-strength steel can reduce the thickness of the material, so compared with ordinary steel plates, the cost can be increased without a substantial increase, about 1.5 times that of ordinary steel plates.
The density of aluminum alloy is 2.68g/cm³, which is only 1/3 of that of steel plate. Considering the need to increase the thickness and cross-section of aluminum, the weight can be reduced by 30% to 50%. Compared with steel plates, the cost of general aluminum plates will increase by 2-5 times.
The density of carbon fiber composite material is 1.5 g/cm³, which is less than 1/5 of steel. Carbon fiber composite materials applied to car doors, engine compartment covers and trunk lids can reduce weight by more than 50%, and their material costs have increased by more than 5 times compared to steel plates.